Differences with other surface treatment methods
There are various techniques other than blasting for doing surface treatment.
We will explain the features of each method and the differences with wet blasting.
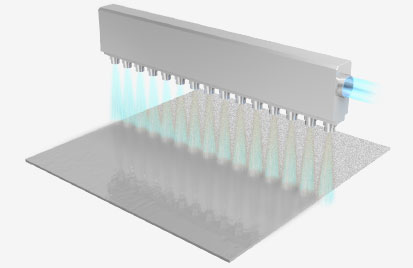
Sandblasting
Sandblasting is a blasting method that uses compressed air from a compressor as energy for accelerating particles. Generally, blasting is often referred to as sandblasting.
Unlike wet blasting, no water is used.
Since a wide variety of particles can be used, it can be applied to various applications. However, unlike wet blasting, if there is any oil or moisture on the surface to be treated, degreasing and drying are required in advance.
In addition, since the blasted abrasive material easily scatters and turns into dust, it is necessary to take precautions against fire and to install equipment such as a dust collector.
Wet blasting, which uses water as its medium, generates almost no dust.

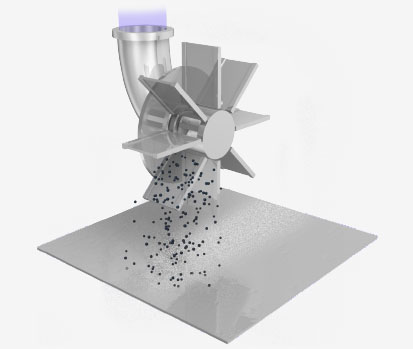
Shot Blasting
Shot blasting is a method in which an impeller is rotated by a motor, and its centrifugal force is used to accelerate and project particles.
It is similar to sandblasting, but does not require a compressor, saving energy and cost.
In addition, a large amount of particles can be projected over a wide area, and it is good at uniform treatment of large areas.
However, in order to suppress scattering during blasting, the particles must have a certain size (mainly about 1 mm) and mass.
Unlike wet blasting, there are fewer types of abrasives to choose from, and the type of processing is also limited.
And in general, it is not suitable for high-precision processing.
This is also a big difference with wet blasting, which excels at precision processing.
Chemical Etching
There are various type of surface treatment processes, such as plating, chemical processing, pickling, and polishing that use chemicals.
However, this section describes chemical treatments such as etching, roughening, and cleaning that achieve this through chemical reactions.
Chemical treatment enables uniform treatment of the entire surface regardless of the shape of the workpiece, does not require special equipment, and is inexpensive.
However, there are disadvantages such as the need to use different liquids depending on the material and purpose, the need to consider safety for some chemicals, the difficulty of quality control, and the generation of chemical reaction waste and wastewater.
Naturally, these chemical processing disadvantages do not occur in wet blasting, which is a physical processing method.
Plasma
Plasma is a state in which atoms and molecules are ionized and separated into positive ions and electrons by continuously applying energy to the gas using a high-voltage power supply.
Plasma treatment is a process in which a specific gas is made into a plasma state and brought into contact with an object to cause a chemical reaction on the surface.
Plasma treatment is a process that performs hydrophilization, cleaning, or processing.
Plasma treatment can be applied to a wide variety of materials, including resins, metals, glass, and films, and can be applied to objects with complex shapes. However, its effectiveness diminishes over time.
In addition, exhaust equipment is required because the processing generates ozone.
Surface treatment by wet blasting, which physically processes an object, does not have the above-mentioned time dependency.
Scrub Jet
Like wet blasting, the scrub jet uses a slurry which is a mixture of particles and a liquid. However, a pump is used instead of compressed air, and processing is done by spraying only using water pressure.
A favorable work environment free of dust, which is an advantage of the wet type, can be obtained.
Compared to wet blasting, it does not use compressed air, so it is technically simpler and costs less overall.
However, since the projection speed is slower than wet blasting, it is almost impossible to process the target surface when using small particles of a few microns in size.
Water Jet
Water Jet is a technology for processing objects by compressing water and jetting it at high speed from a thin nozzle. Since it is only water, the cost is relatively low and no dust is generated.
However, since the water used for processing contains the elements of the target workpiece, wastewater treatment is required.
The water is jetted at very high pressure, with the maximum being 2000kg/cm2, and the water jetted at 200 MPa is a solid rod as hard as iron.
It is mainly used to cut objects or to scrape off the surface of the workpieces.
Since it does processing only with water, post-processing is easy. However, its weaknesses compared to wet blasting are that its force is too strong and it is not good at processing large areas.