Scraping of the build-up substrate
Processing Details
- Scraping
Fine surface processing by wet blasting
Physical processing, which allows the filler-containing resin layer on the build-up substrate surface to be processed uniformly at high speed.
Process Objective
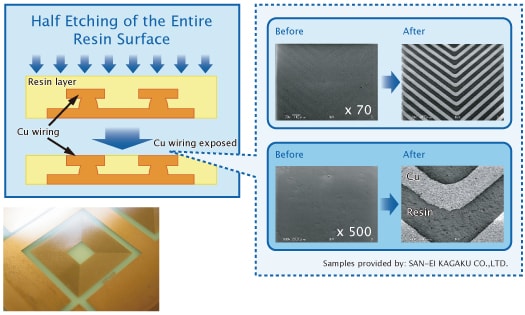
- Surface is exposed by removing a very thin layer of the surface of the substrate on which electric parts are embedded.

- Grinding of the resin on the surface of the substrate and only the circuits are left on it.

Problems with conventional processing methods
| Dry Etching (Plasma) |
|
|---|---|
| Laser |
|
| Machining |
|
Processing Image
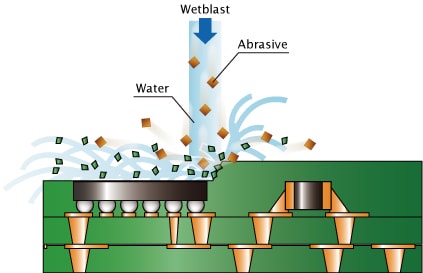
The Copper Wiring's Exposure According to Wet Blasting
Features
- Half-etching of the entire surface for the filler-contained resin.
- Process selection of the resin to reduce Copper etching.
Processing of undercoat materials
- Patterning using copper as a mask.
- High accuracy by anisotropic processing.
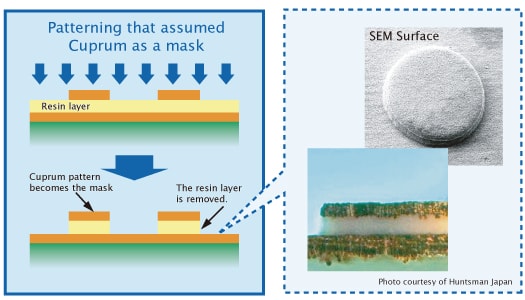
- Possible to alleviate (reduce) damage to conductors by processing with resin abrasives or super fine aluminum oxide abrasives.
Processing Condition
| Abrasive Used | Alumina A#2000 |
|---|---|
| Air Pressure | 0.25 MPa |
| Processing Speed | 20 mm/sec |
| Projection (Spray) Angle | 90° |
| Number of Passes for Processing | 4-10 passes |
Example of the formation of an embedded capacitor
- Patterning using copper as a mask.
- High accuracy by anisotropic processing.







